10 Components of Business Intelligence (With Examples)
Money.hajijatim.id – In the dynamic and data-driven landscape of modern business, the ability to gather, analyze, and derive actionable insights from vast amounts of information is paramount. This is where Business Intelligence (BI) takes center stage. Business Intelligence encompasses a range of tools, technologies, and strategies that empower organizations to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and gain a competitive edge in the market. To unlock the full potential of Business Intelligence, it is crucial to understand its core components and how they work together to drive success. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the comprehensive components of Business Intelligence, shedding light on their significance and unveiling the power they hold.
1. Data Sources: The Wellspring of Insights
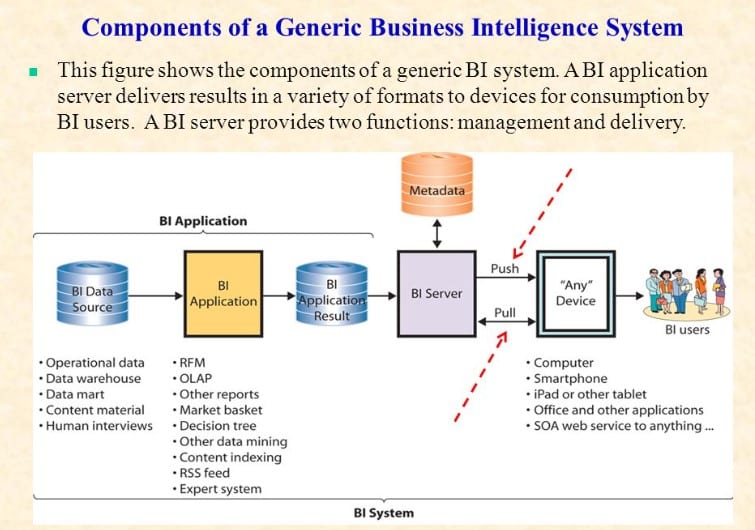
At the heart of Business Intelligence lies the data sources that fuel the entire process. These sources can be internal, such as transactional databases, customer records, or sales data, or external, including market research reports, social media feeds, and third-party data. A diverse range of data sources allows organizations to gain a comprehensive view of their operations, customers, and market dynamics.
- Example: A retail company collects data from various sources, including point-of-sale systems, customer loyalty programs, and online transactions. By integrating this data, they gain a comprehensive understanding of customer behavior, sales trends, and inventory management.
2. Data Warehousing: Structured Storage for Insights
To effectively harness the power of data, organizations rely on data warehousing. A data warehouse serves as a centralized repository that consolidates and organizes data from various sources into a structured format. This structured storage enables efficient querying, analysis, and reporting, providing a solid foundation for Business Intelligence initiatives.
- Example: A healthcare organization integrates patient data from electronic health records, diagnostic systems, and wearable devices. By combining this data, they create a holistic view of patient health, enabling personalized treatments and proactive care management.
3. Data Integration: Bridging the Gap
Data integration plays a vital role in Business Intelligence by ensuring that data from different sources seamlessly flows into the data warehouse. It involves processes such as data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) or real-time data integration techniques. By bridging the gap between disparate data sources, organizations can achieve a unified and holistic view of their operations.
- Example: An e-commerce company utilizes a data warehouse to store and analyze vast amounts of customer data, including browsing behavior, purchase history, and demographic information. This centralized data enables them to personalize marketing campaigns, improve product recommendations, and optimize the customer experience.
4. Data Modeling: Building the Blueprint
Data modeling involves designing the structure and relationships of the data stored in the data warehouse. It includes defining entities, attributes, and their interconnections through entity-relationship diagrams or dimensional modeling techniques like star or snowflake schemas. Effective data modeling ensures data accuracy, consistency, and enables efficient analysis and reporting.
- Example: A financial institution uses data modeling techniques to create a dimensional model that captures customer transactions, account balances, and market data. This model helps analysts uncover relationships between different variables, such as customer demographics and investment preferences, leading to more targeted financial products and services.
5. Data Analytics: Unleashing Insights

The true power of Business Intelligence lies in data analytics. This component encompasses a wide range of techniques, including descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing historical data, while diagnostic analytics delves deeper to identify the reasons behind specific outcomes. Predictive analytics leverages statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future trends, and prescriptive analytics provides recommendations to optimize decision-making.
- Example: A transportation company analyzes historical and real-time data from sensors embedded in their vehicles. By applying predictive analytics, they can identify patterns of vehicle maintenance issues and proactively schedule repairs, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
6. Reporting and Dashboards: Visualizing the Story
Business Intelligence thrives on effective data visualization. Reporting tools and dashboards provide visual representations of data analysis results in a concise and easily understandable format. They enable stakeholders to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track progress, and gain insights at a glance. Interactive dashboards empower users to explore data, drill down into details, and make data-driven decisions with speed and agility.
- Example: A marketing agency creates interactive dashboards to track key marketing metrics such as website traffic, social media engagement, and campaign performance. This visual representation enables marketers to monitor the effectiveness of their strategies, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions in real-time.
7. Data Governance: Ensuring Trust and Compliance
Data governance ensures the quality, security, and integrity of data throughout its lifecycle. It involves establishing policies, procedures, and guidelines for data management, data privacy, and regulatory compliance. Data governance frameworks facilitate data stewardship, data lineage tracking, and enforce data standards, fostering trust in the accuracy and reliability of Business Intelligence outputs.
- Example: A global organization implements data governance policies to ensure compliance with data protection regulations. They establish roles and responsibilities for data stewards, define data quality standards, and enforce data privacy rules, ensuring the ethical and responsible use of customer data.
8. Data Mining: Discovering Hidden Gems of Insights

In the vast landscape of data, hidden gems of insights lie beneath the surface. Data mining is the process of extracting valuable patterns, trends, and relationships from large datasets. Through techniques like clustering, classification, and association analysis, organizations can uncover valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making and uncover hidden opportunities.
9. Data Visualization: Painting a Picture of Insights
Data visualization brings Business Intelligence to life by transforming complex data into intuitive and visually appealing representations. Through charts, graphs, and interactive visualizations, organizations can communicate data-driven insights in a compelling and engaging manner. Data visualization enhances understanding, promotes data exploration, and enables stakeholders to grasp the bigger picture effortlessly.
- Example: An e-commerce company uses data visualization techniques to create intuitive charts and graphs that illustrate sales trends, customer demographics, and product performance. These visualizations enable executives to quickly grasp key insights and make informed decisions that drive revenue growth.
10. Data Security: Safeguarding the Treasures With data being a precious asset, ensuring its security is of utmost importance. Data security measures protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential risks to data confidentiality. Robust security protocols, encryption, access controls, and regular audits are essential components of a comprehensive Business Intelligence strategy.
As organizations strive to harness the power of Business Intelligence, understanding and leveraging these core components becomes crucial. By integrating diverse data sources, implementing robust data warehousing, harnessing the power of analytics, enabling effective reporting and visualization, ensuring data governance and security, and embracing data mining and data modeling techniques, organizations can unlock the full potential of Business Intelligence. Elevate your organization’s decision-making, drive operational excellence, and pave the way for a competitive edge in the data-driven era.
